Hi All, in this series i am going to be looking at a deepdive into the Zerto Cloud Manager(ZCM), the ZCM is a component normally deployed by our service providers but can equally be used by End User customers aswell.
Some of the features the ZCM brings are:
- Multi-Tenancy Support
- Resource allocation
- Organisations or “ZORG” Definition
- ZSSP user configuration
- Granular RBAC
- ZCC deployment
- Service Profile Definition
- Centralized alerting – can also be viewed via Zerto Analytics
As you can see there is a wealth of additional features and functionality that can be added to the Zerto platform with the addition of the ZCM
Deployment
As we can see the ZCM is another VM deployed inside the Datacenter – the install packages can be downloaded via MyZerto.
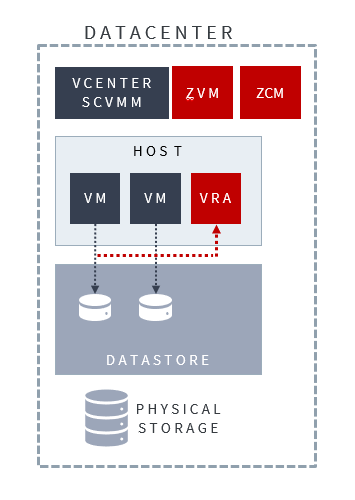
For all tech specs and ports etc please follow the Zerto official documentation :
Walkthrough
In this section I will be walking you through the various areas of the ZCM to give you an understanding of what each section does
but first lest get some Jargon out of the way
- ZORG – Zerto organisation – Used to define what a single tenant is inside of the Zerto Infrastructure
- ZSSP – Zerto Self Service Portal – Allows tenants to access Zerto Infrastructure that is not hosted by themselves
- ZCC – Zerto Cloud Connector – A Small Appliance that allows a dedicated connection point for each Tenant, this masks the infrastructure behind the ZCC so no information is displayed to the tenant.
Login
Logging in is simple – its a Web based UI – that is accessed using the following URL:
htps://zcmfqdn:9989
Organizations Tab
In this section we show all the ZORG’s that are currently configured inside the ZCM, as the ZCM is a global entity across the entire Zerto estate a ZORG only needs to be created once and can now be used across the entire Zerto estate wherever it is required.
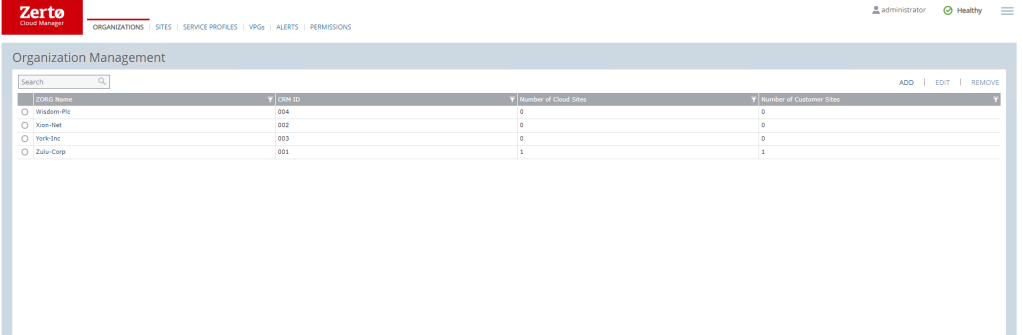
We can also drill into the each organization in more detail – we will cover this further down.
Sites Tab
The sites listed under this screen are the Sites directly connected to this ZCM – this does not include DRaaS Customer connected via a ZCC.
You will see all the various info about the site including whether it is configured for VCD or not.
Adding a new site is very easy
Simply click on add, input the required details – ZVM IP the port you have installed the ZVM on – normally left as default, and the ZCM access code which can be found under the site settings in your ZVM.
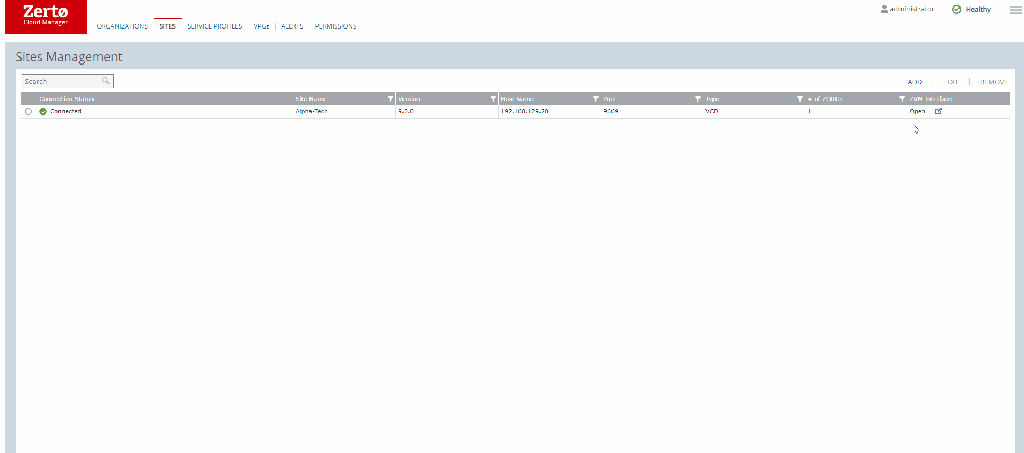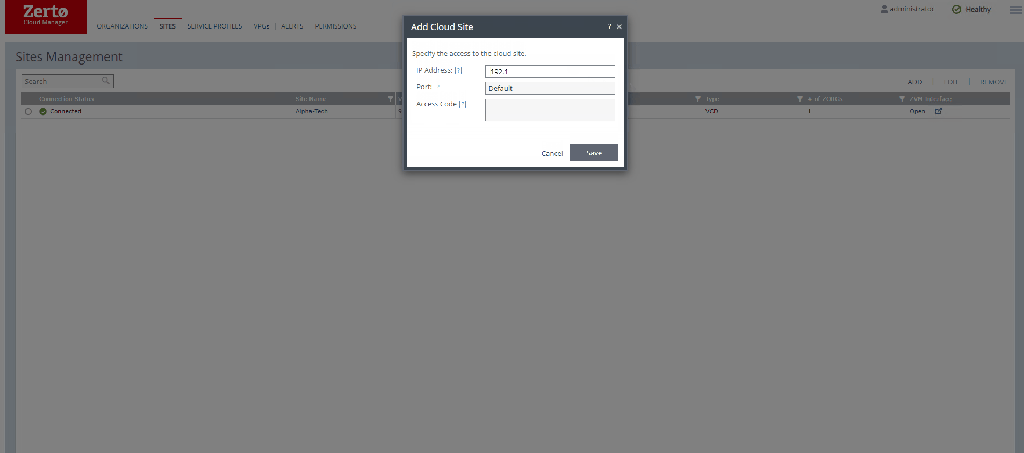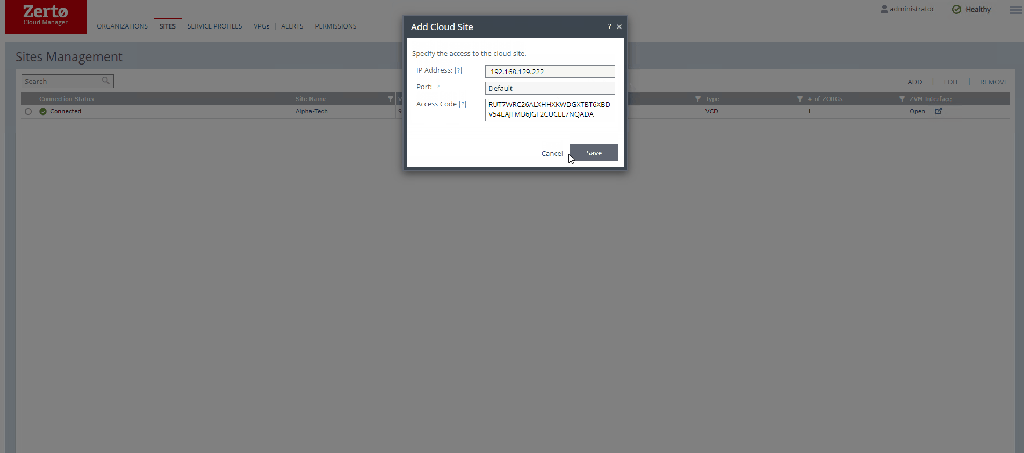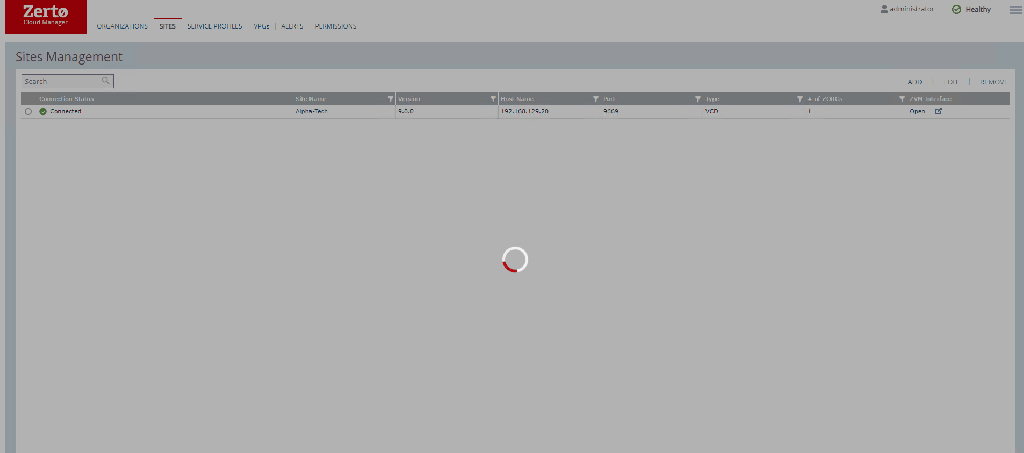
Service Profiles
Service Profiles come in extremely handy for either Service providers of Large enterprises that want a cookie cutter approach to protecting their VM’s. Service profiles allow the administrator to pre-define certain fields inside of a VPG.
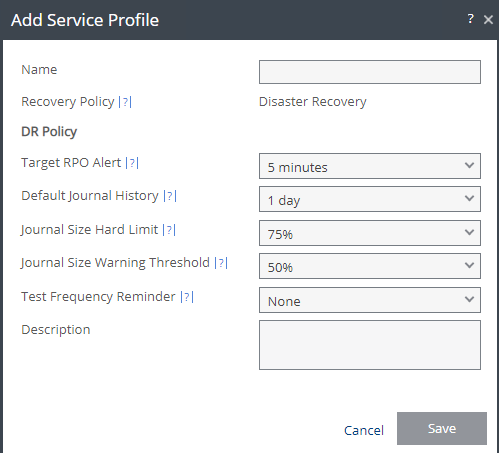
The fields that are pre-populated in a service profile are:
- Target RPO Alert – The threshold for when Zerto should alert the user that an RPO has exceeded expected RPO
- Default Journal History – The time of length that the short term journal is configured for.
- Journal Size Hard Limit – Maximum size the short term journal can grow to in % of VM size
- Journal Size Warning Threshold – the % Size of the journal that will trigger an alert
- Test Frequency Reminder – how often should this VPG be tested for DR
These service profiles are then assigned during the VPG Creation ensuring that each VPG has the same settings per service profile.
Permissions
The Permissions tab is where administrators will configure RBAC.
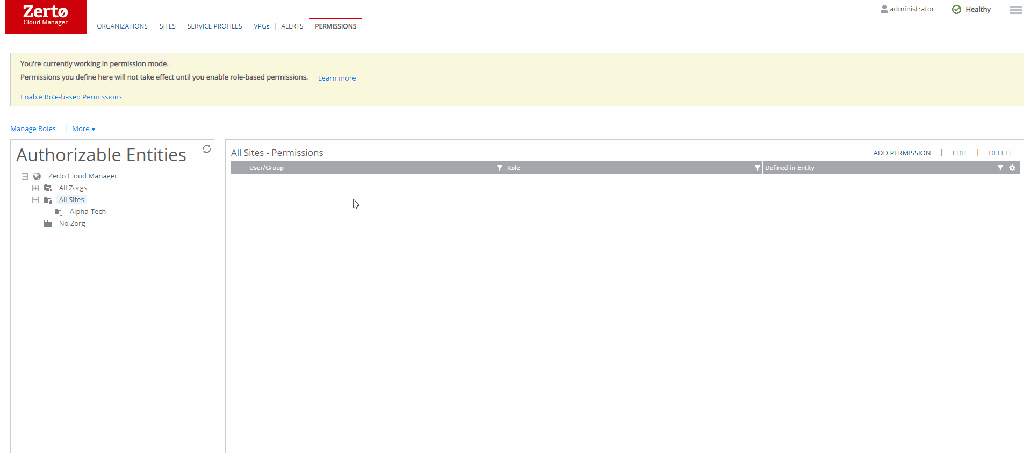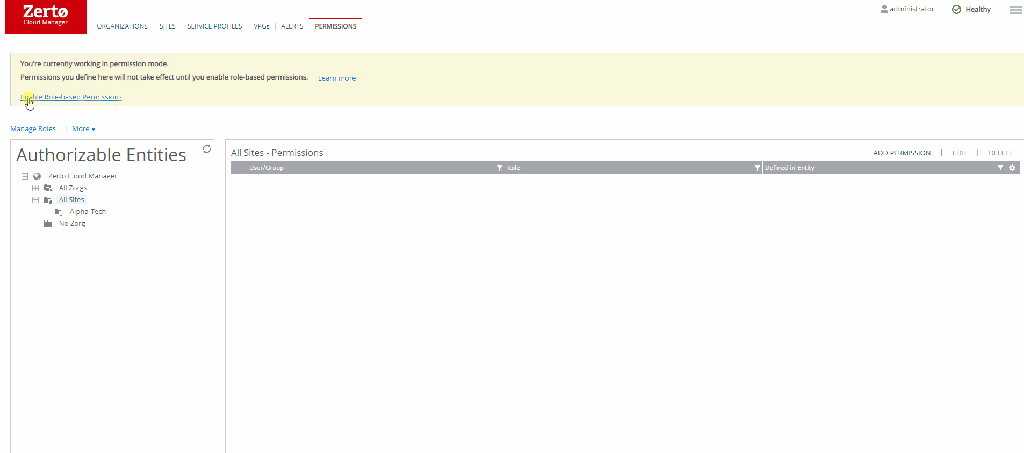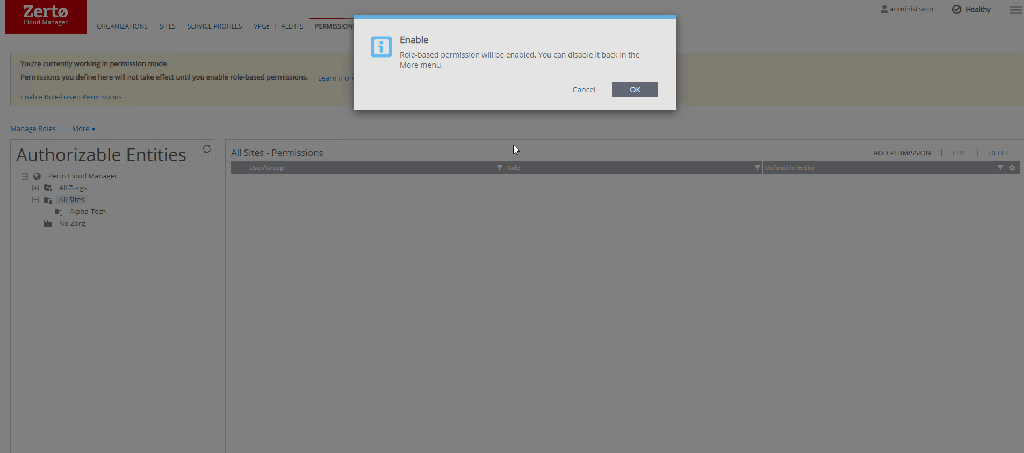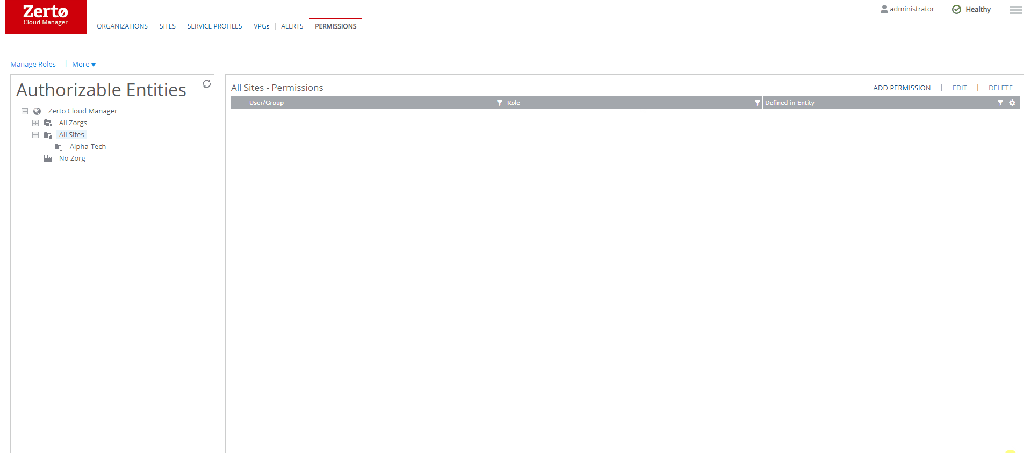
To enable RBAC select the “Enable Role-Based Permissions” option
I will be doing a follow up blog to cover RBAC in more detail so watch this space.
Deep Dive into ZORGS
as we discussed earlier a Zorg is an organisation inside of Zerto, so let’s explore one in more detail :
Zorg Page
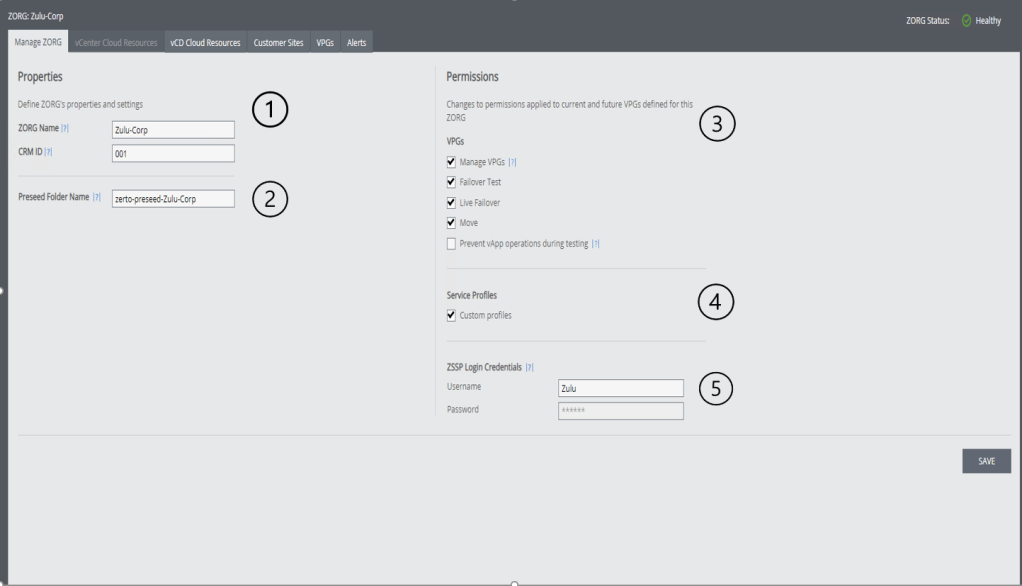
Lets run through each section in a little more detail:
1– This is the Zorg information – this will be used for Zorg identification both internally and externally, this is also used as a field for the ZSSP login
2– Pre-seed folder name is used to store ZORG pre-seed disks, this means that only Disks inside of a folder that matches this name can be seen by a ZORG to use for pre-seed – make sure this matches a folder name inside your environment if you change it.
3-These permissions dictate what a customer can/cant do inside of the ZSSP – they are relatively self explanatory, expect for the last one – “Prevent vAPP operations during test” , when this is turned on a user will not be able to change settings inside of the created VCD vApp when Zerto is performing a failover test. This prevents issues where users could delete the vApp without zerto being aware making the VPG go into an error state, in my opinion this should always be turned on.]
4– Custom Service profiles allows a ZORG to create their own service profiles on a per VPG basis, this enabled a ZORG user to change the settings we ran through earlier in the post.
5– ZSSP login credentials – Again self explanatory – these are the credentials used for a ZORG to login to the ZSSP, I would recommended rotating credential’s on a regular basis for security purposes.
Resource Allocation
One of the most important sections in the ZCM is the ability to assign resources to a ZORG ensuring that no Zorg can use resources they have not been assigned. a ZVM can either be configured to use vCenter OR VCD this shows in the sites tab I showed earlier.
vCenter Resources that can be assigned are the normal objects found in vCenter these comprise of:
- Resource Pools – These are mandatory when deploying Zerto in multi-tenant vCenter environment – can only exist in a single ZORG
- Virtual Networks – Can only Exist in a single ZORG
- Datastores – Can exist in multiple ZORG’s
- Repositories – can only Exist in a single ZORG
When we are using VCD we add the whole VCD organisation under the ZORG – This will then automatically include all ORG VDC’s and the objects contained within them, eg ORGVDC Networks and Storage policies. each organisation can only exist in a single ZORG at a time, and the ZORG will populate new resources as they are added into the VCD organisation.
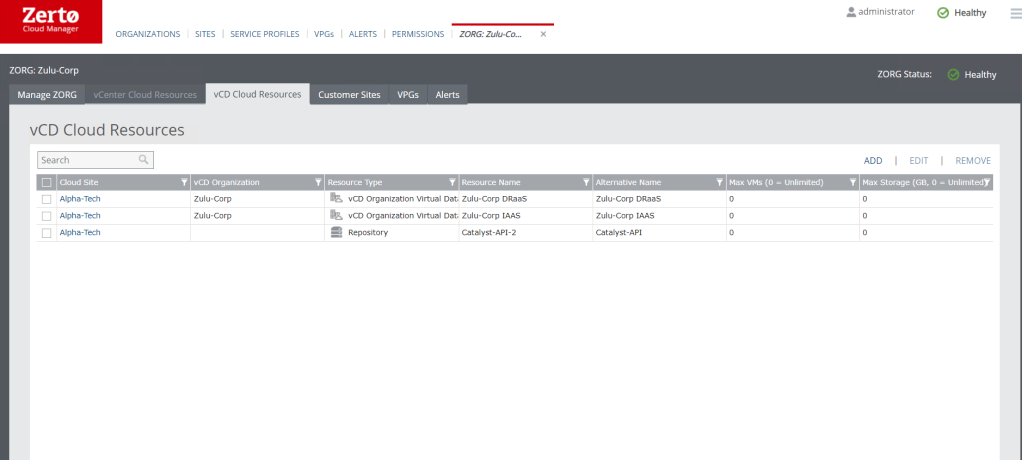
Customer Sites
This section is where we would Deploy ZCC’s for the specified ZORG
There is a simple wizard to help deploy the appliances that connect a customers on-premise site to a service provider site.

Once this is deployed the Zorg customer can now pair through the ZCC into the ZVM backing it, this hides all internal infrastructure outwards.
Conclusion
the ZCM is a very powerful component and probably a component that some of you may not have used before and can be used in service provider and Large enterprise customer settings.
As I said before keep an eye out for more details on the RBAC post to follow
Please share and comment
Cheers
Chris